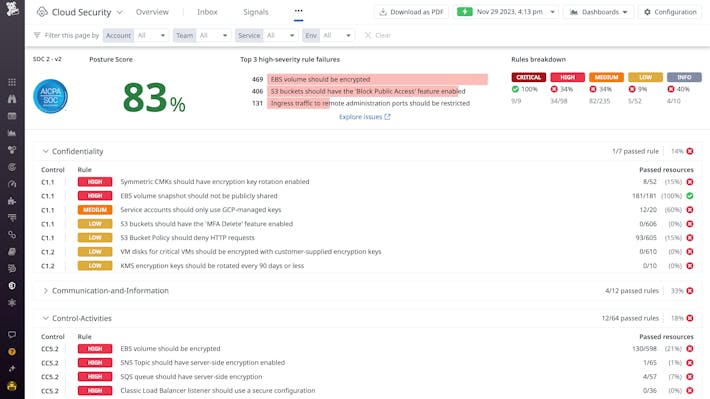
Cloud security monitoring gathers logs, metrics, and events from every corner of your cloud infrastructure, including virtual machines, containers, identity systems, network flows, and applications, to build a real‑time picture of how your environment behaves.
By continuously supervising and analyzing that data, teams can detect unauthorized access or misconfigurations before breaches occur. With clear alert workflows and automated playbooks in place, monitoring security becomes part of daily operations rather than weekend firefights.
What Is Cloud Security Monitoring?
Cloud security monitoring is the practice of continuously observing and analyzing cloud‑native resources, such as compute instances, storage buckets, serverless functions, and network controls, to detect threats, vulnerabilities, or compliance gaps in real time.
It works by aggregating network telemetry from firewalls and security groups and deploying lightweight data collectors on virtual machines and containers, tracking:
- Logs from virtual machines and containers
- API requests and authentication events
- Network flows, DNS queries, and endpoint connections
- System health metrics and performance stats
- User behavior across environments
Those data streams feed into a centralized analytics engine, often a SIEM or XDR platform, that normalizes log formats, applies correlation rules, and runs behavioral analytics to highlight outliers. Instead of juggling separate consoles, teams gain a single pane of glass where alerts are prioritized, tickets open automatically, and remediation scripts can run without manual steps.
What are the Core Components of Cloud Security Monitoring?
Every security setup relies on a few fundamental building blocks. In a cloud environment, these elements act like sensors, filters, and alarm bells; they collect data, highlight odd behavior, and trigger rapid responses.
- Data collectors and agents on VMs, containers, and serverless workloads
- Log aggregation pipelines supporting multiple clouds with normalized schemas
- Anomaly detection engines leveraging machine learning to spot deviations in usage
- Alert workflows integrated into ticketing and automation platforms
Together, these pieces deliver full-spectrum coverage: raw telemetry is gathered, normalized, analyzed for anomalies, and then turned into clear action items. This approach lets your team zero in on real threats instead of wading through endless noise.
Importance of Cloud Security Monitoring
Cloud security monitoring plays a pivotal role in protecting digital operations, and in 2025, cloud attacks are faster, sneakier, and better funded than ever before. This is why cloud security monitoring is so important:
- No blind spots: From on‑premise to multi‑cloud, you maintain end‑to‑end visibility.
- Insider threat detection: Tracking privileged user actions unveils misuse before it escalates.
- Data‑driven insights: Historic trend analysis exposes policy gaps or shadow IT resources.
- DevSecOps enablement: Discover misconfigurations in CI/CD pipelines rather than in production.
- Reputation protection: Rapid detection and disclosure keep customers confident and regulators satisfied.
But with the growing complexity of cyberattacks, you will need more than just cloud security monitoring; you will also need reliable cybersecurity software.
Benefits of Cloud Security Monitoring
Monitoring your cloud without security is like locking your front door but leaving the windows wide open. Pairing security and monitoring is how modern teams stay safe, and here’s why:
- Proactive threat detection: Sudden traffic spikes? Odd login times? Unfamiliar IP addresses? Automated rules flag unusual traffic spikes or off‑hours login attempts so you catch attacks early.
- Faster incident response: Integrating alerts into chatops or ticketing cuts mean‑time‑to‑detect significantly, since analysts no longer chase logs across multiple consoles, and alerts connect directly to your automation tools. By the time your team is notified, the malicious instance is already isolated.
- Simplified compliance: cloud compliance monitoring funnels audit logs (including everything from privilege changes to API events) into unified, ready‑made reports for standards like PCI‑DSS or HIPAA, saving hours of manual work.
- Cost avoidance: Early alerts about open storage buckets or overly‑permissive roles prevent expensive breach investigations and fines.
- Scalable oversight: Cloud-based monitoring software handles metrics from dozens of accounts without extra headcount, tracking hundreds of resources with the same visibility you had at ten.
- Threat pattern detection: Continuous security monitoring reveals slow, quiet attacks—subtle permission escalations, lateral movement, insider abuse.
- Unified view: A single dashboard enforces consistent security and monitoring policies across AWS, Azure, GCP, and private clouds.
Key Features of Advanced Cloud Monitoring Solutions
These cloud monitoring solutions feature a balance of performance metrics (CPU, memory, network) and security events (failed logins, policy violations), giving you a 360° view of risk.
- Cloud security monitoring tools with prebuilt connectors for AWS, Azure, and GCP, cutting integration time substantially.
- Continuous security monitoring captures events 24/7 without manual steps.
- Behavioral analytics that learn normal patterns and reduce false positives by focusing on real anomalies.
- Automated remediation scripts or serverless functions to isolate compromised resources and disable accounts in seconds.
- Custom dashboards for executives, compliance teams, and security analysts, each with tailored views, drill-downs, and to flag your own use-case-specific behavior.
- Integration hubs that connect vulnerability scanners, threat intelligence feeds, and service‑desk tools for holistic visibility.
- Compliance reporting with prebuilt dashboards (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI-DSS).
These features are what make cloud monitoring security more than a firewall or antivirus add-on; it becomes an active control layer over your entire cloud and cloud vulnerabilities.
Challenges of Cloud Security Monitoring
These are the most common headaches teams run into, no matter how good their tools may be:
- Data volume overload: Capturing every log from dozens of services strains storage and analytics pipelines. Implement sampling and filtering to reduce noise.
- Alert fatigue: Excess low‑severity notifications can drown out critical threats. Regularly tune thresholds and suppression rules to keep noise down.
- Multi‑cloud complexity: Each provider uses unique log formats. Adopting a common schema like OpenTelemetry helps normalize data across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Skill gaps: Writing effective correlation rules and fine‑tuning analytics engines demands expertise that’s in short supply. Managed services or training programs can help bridge that gap.
- Latency concerns: Batch log uploads may delay alerts. Streaming ingestion architectures offer lower latency for quicker response.
Overcoming Roadblocks
- Use open standards like OpenTelemetry for unified logging
- Rate‑limit or sample high‑volume sources at the edge
- Document runbooks that tie alerts to automated containment steps
These tactics help mature your security and monitoring ecosystem into a proactive defense posture. For private setups, you might want a private cloud.
Best Practices for Cloud Security Monitoring
Even with the best system, you still need to follow the best practices for cloud monitoring. The good news is that they’re pretty easy to repeat:
- Define clear playbooks: Map each alert to a response (notify, isolate, or escalate) so your team knows exactly what to do.
- Automate remediation: Integrate with infrastructure‑as‑code or serverless functions to block malicious IPs or rotate compromised credentials automatically.
- Enforce least privilege: Restrict who can modify monitoring security rules or access raw logs, reducing insider risk.
- Review rules regularly: As your cloud footprint evolves, prune outdated alerts and adjust thresholds to match new baselines.
- Integrate posture management: Link cloud compliance monitoring checks with continuous security monitoring for end‑to‑end coverage.
- Adopt cloud monitoring best practices: Combine performance and security data into unified dashboards to give DevOps and SecOps a shared view.
Sample Onboarding Checklist
- Enable default logging on every new VM or container
- Encrypt log streams in transit to your SIEM/XDR
- Schedule quarterly audits of correlation rules
- Feed vulnerability scanner alerts into your monitoring workflows
By codifying these steps, teams can onboard new workloads without sacrificing visibility or control. All of this creates a tighter security and monitoring process across your environment, be it public, private, or hybrid.
Cloud Security Monitoring Solutions – Types and Examples
Choosing the right cloud security monitoring solution depends on your environment, skill set, and scale. Below are five solution types (cloud‑native, third‑party SaaS, open‑source stacks, CSPM & XDR hybrids, and unified dashboards), each with two recommended tools.
Cloud‑Native Monitoring
Built into major cloud platforms, these services offer turnkey threat detection and integration with provider APIs.
-
AWS GuardDuty:
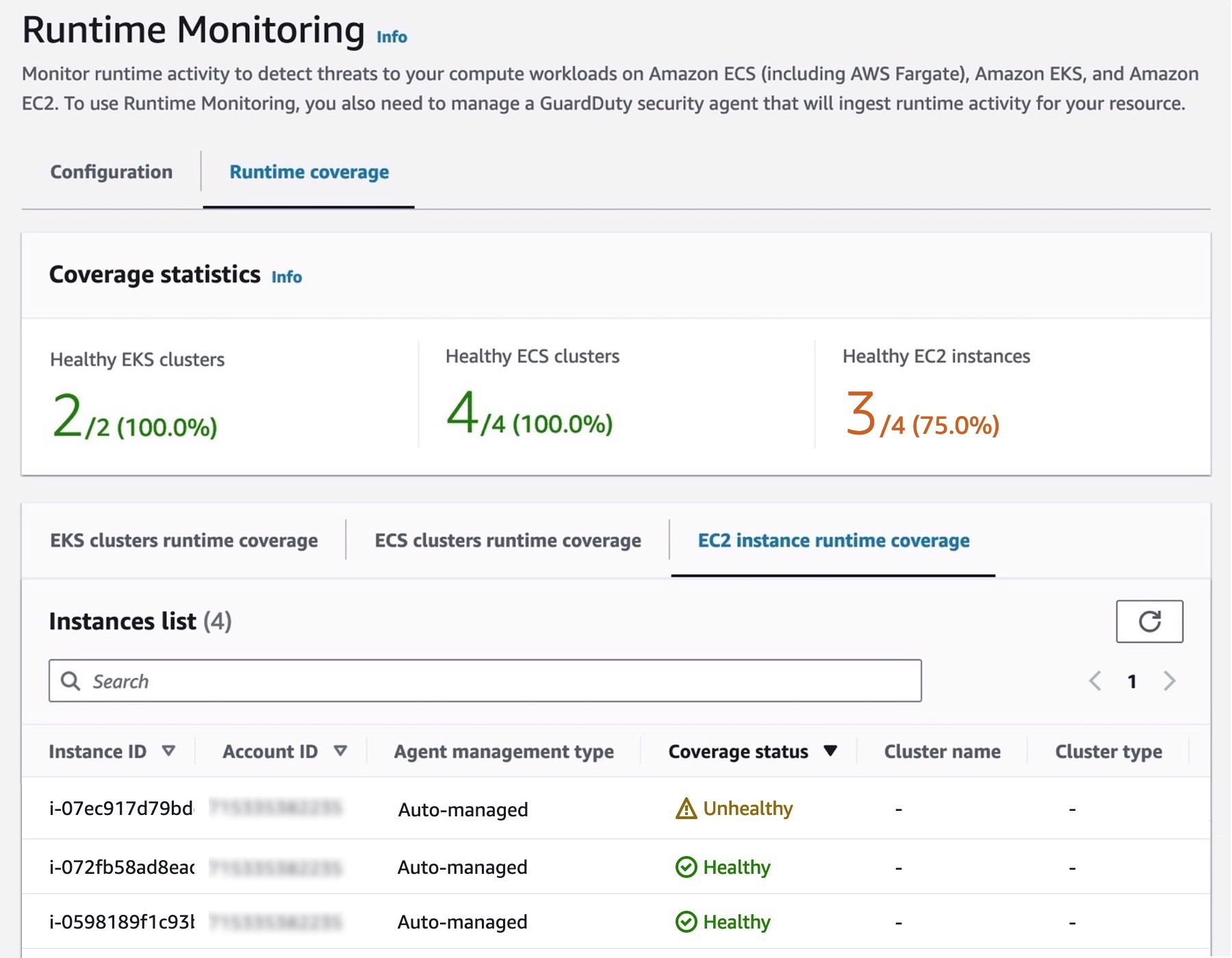
Fully managed threat detection that analyzes VPC flow logs, DNS logs, and CloudTrail events with pay‑as‑you‑go pricing; limited to AWS environments and can generate false positives that require tuning.
-
Azure Sentinel:
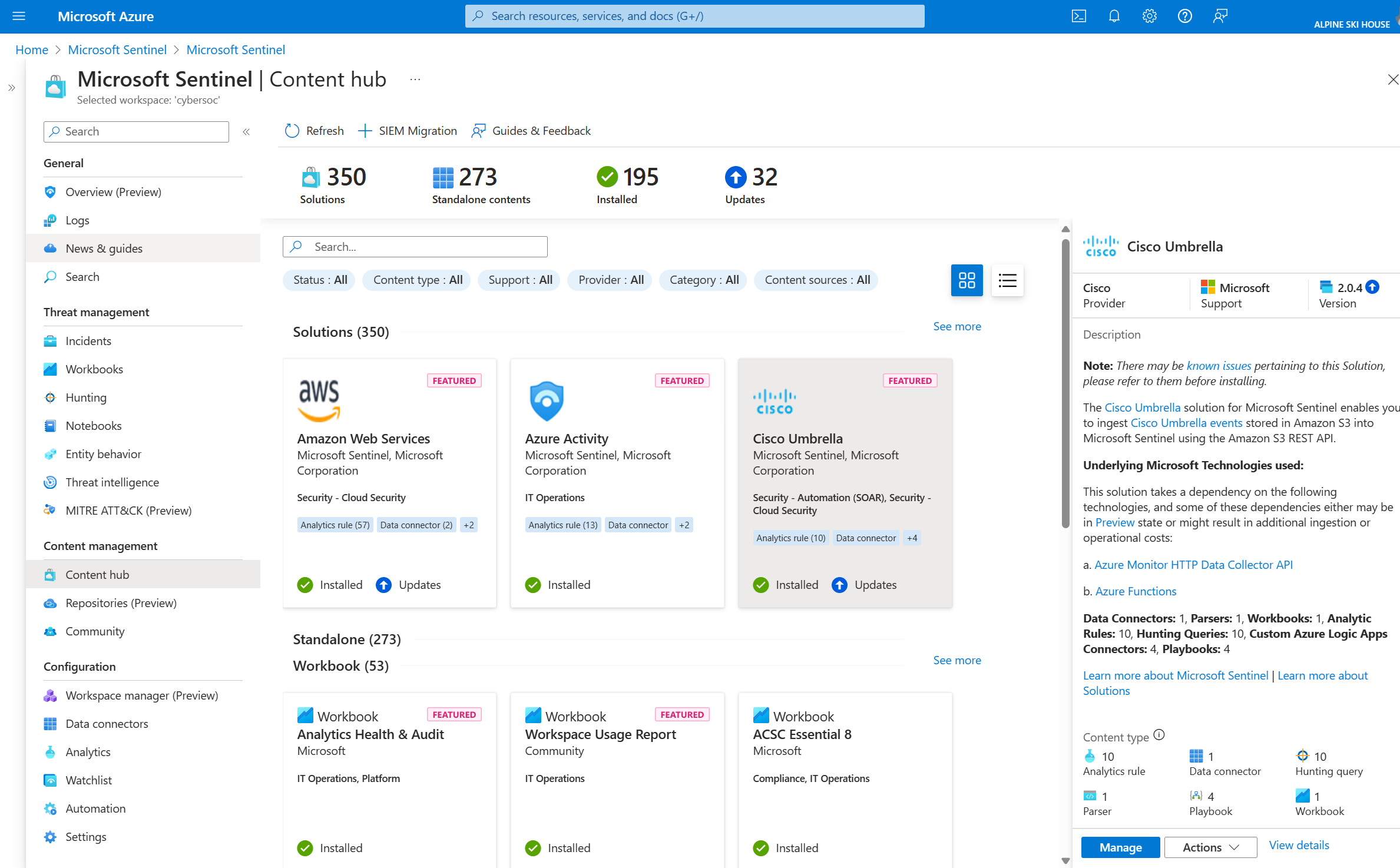
Cloud‑native SIEM/XDR with built‑in connectors for Microsoft services and AI‑driven analytics; unpredictable ingestion costs at scale and a learning curve to fine‑tune alerts.
Third‑Party SaaS
Independent platforms delivering deep analytics, behavior tracking, and automated response, often across multiple clouds.
-
Sumo Logic:
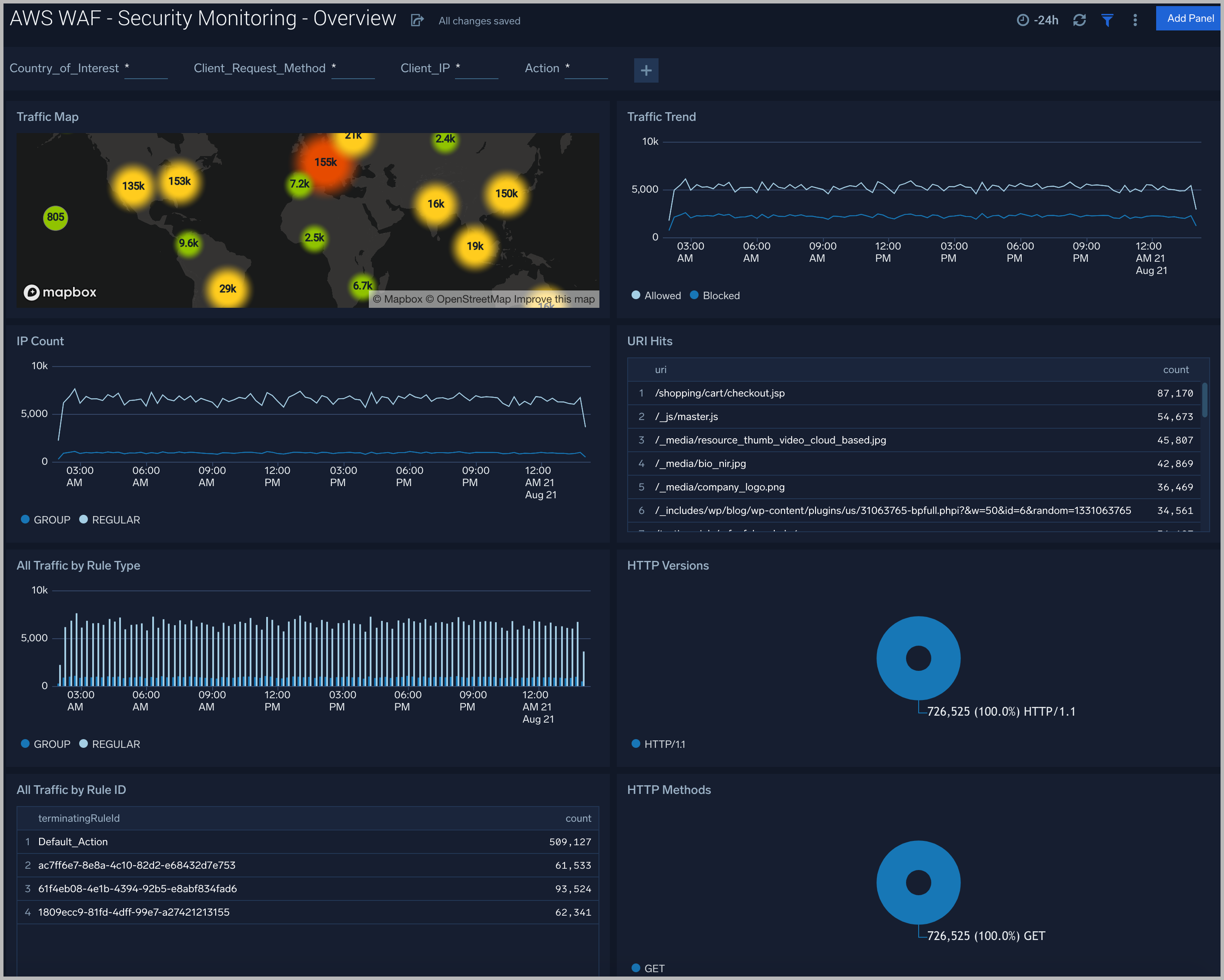
SaaS analytics that ingests cloud‑scale logs and metrics, offering real‑time security insights and compliance dashboards; advanced rule configuration can be complex for new teams.
-
Blumira:
Hosted detection & response with pre‑built playbooks and automated investigation workflows; smaller vendor ecosystem means fewer community integrations and less mature feature breadth.
Open‑Source Stacks
Community‑driven solutions providing full control over data pipelines and analysis, which better suits teams with strong in‑house expertise.
-
ELK Stack:
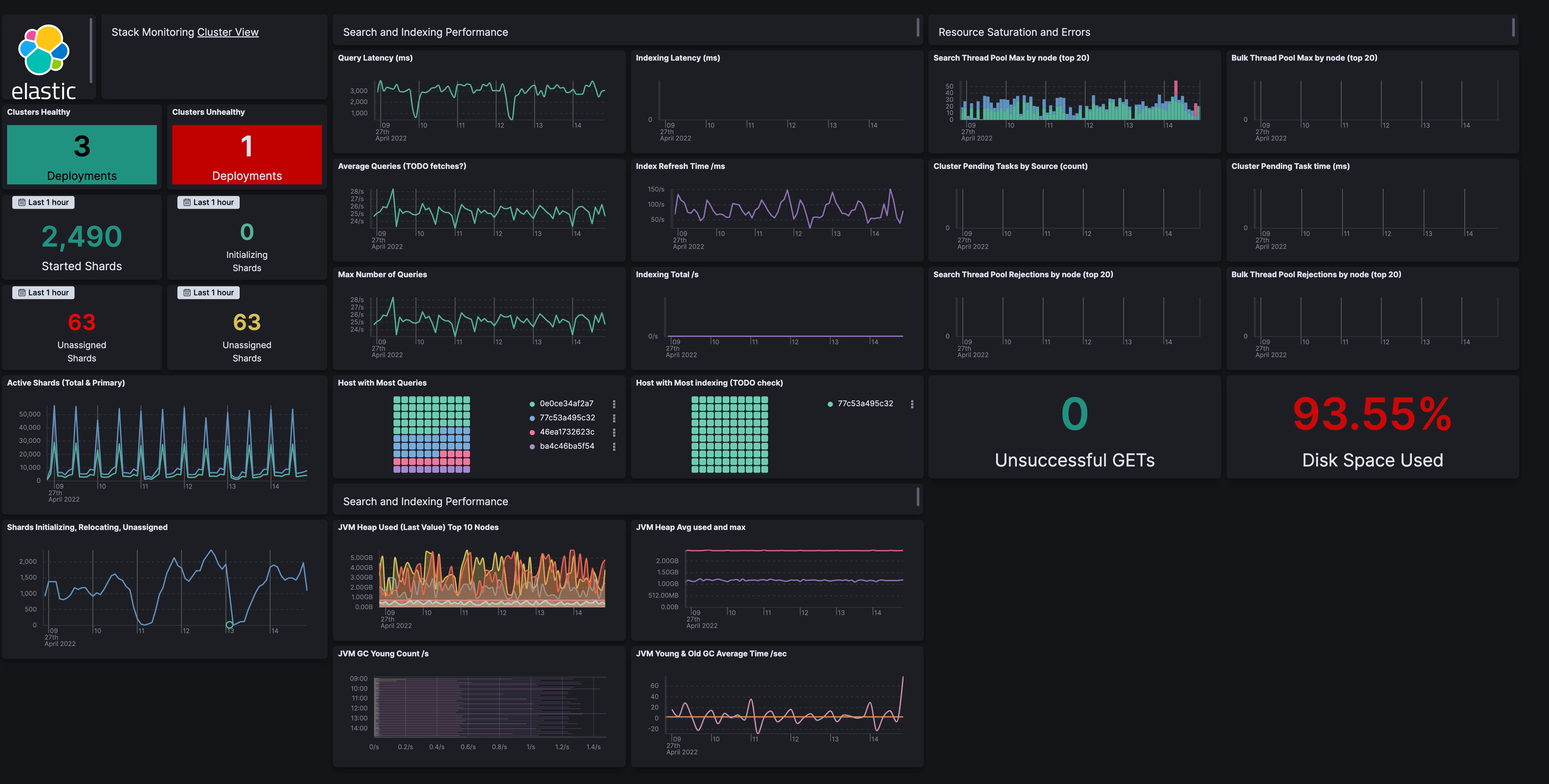
Comprehensive log collection, parsing, and visualization with real‑time dashboards; requires significant setup effort and ongoing maintenance to scale indexing pipelines.
-
Wazuh:
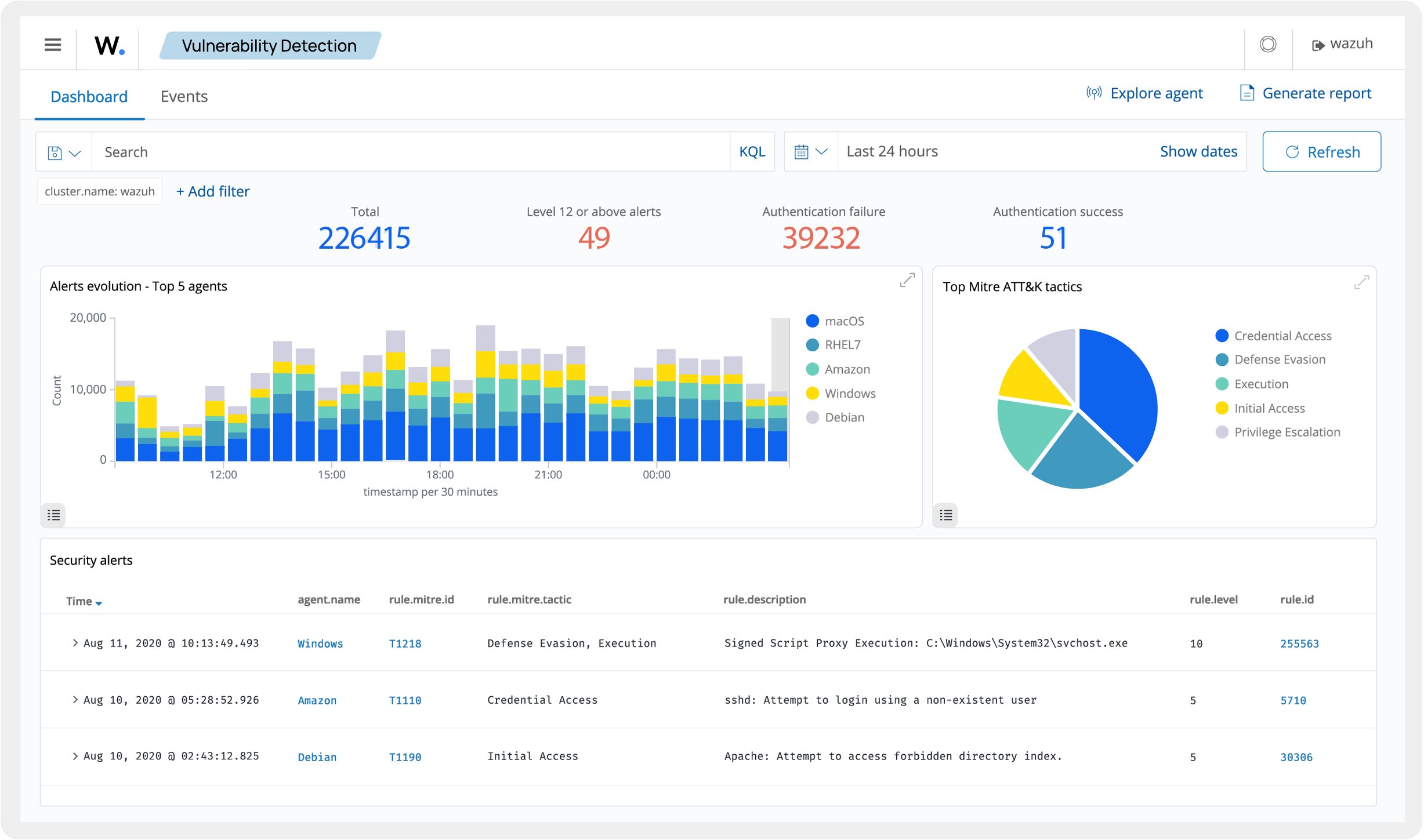
Open‑source security platform extending ELK with host‑based intrusion detection and compliance reporting; steep learning curve and limited official support channels.
CSPM & XDR Hybrids
Platforms that merge continuous posture management with runtime threat detection, giving you both configuration and behavior insights.
-
Prisma Cloud:
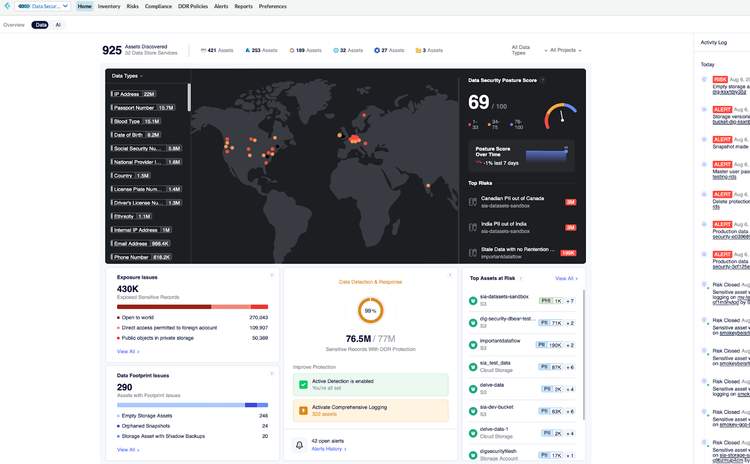
Unified CSPM, CIEM, and runtime defense with container and serverless support; initial setup complexity and a steep learning curve slow down time to value.
-
CrowdStrike Falcon:
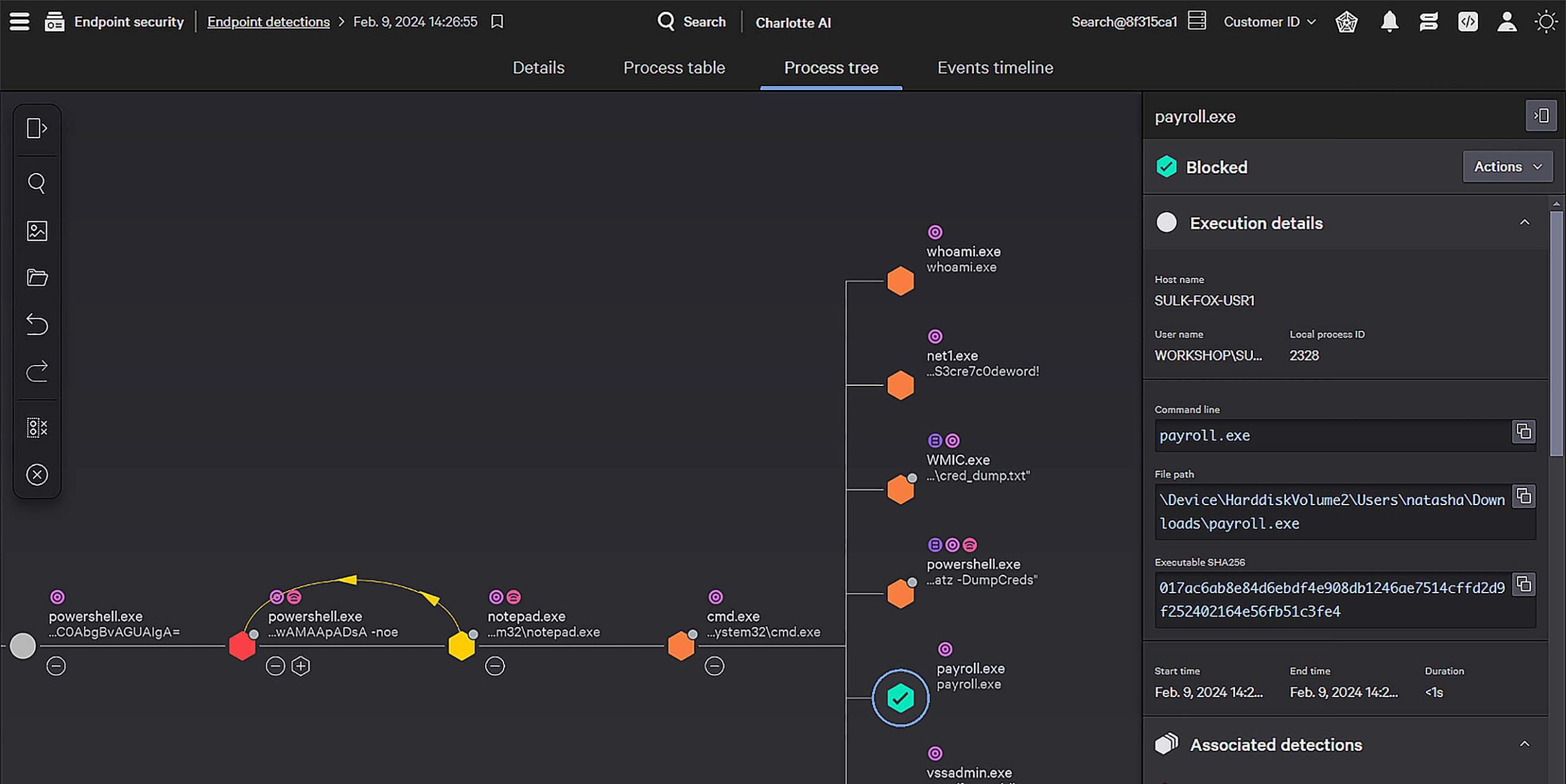
Full‑stack XDR with endpoint protection, vulnerability management, and integrated threat intelligence; performance overhead on endpoints and requires specialized skills for optimal tuning.
Unified Dashboards
Solutions that bring security events, logs, and performance metrics into a single pane of glass, bridging DevOps and SecOps.
-
Datadog:
Combines logs, metrics, traces, and security monitoring modules in one UI, with out‑of‑the‑box alerts for cloud services; complex log ingestion setup and potential for steep data retention costs.
-
Splunk Enterprise Security:
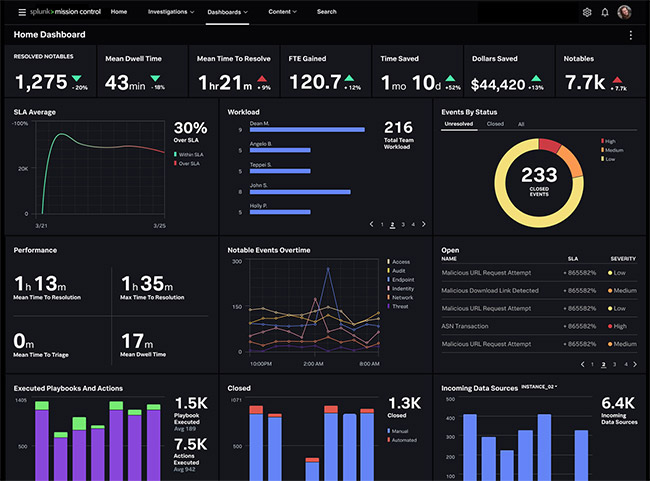
Enterprise‑grade correlation, threat intelligence integration, and customizable security dashboards; premium licensing cost and a high learning curve for new users.
Each category has its trade‑offs, be it the ease of cloud‑native deployments, the customization of open‑source, or the depth of hybrid platforms. Match your choice to your team’s expertise, budget, and regulatory needs to get the most from your cloud security monitoring setup and cloud security architecture as a whole.
Final Thoughts
While a reliable cloud security setup is incomplete without cloud infrastructure security, by incorporating cloud security monitoring tools, monitoring security best practices, and continuous security monitoring into daily operations, you’ll transform reactive log chasing into proactive defense, keeping attackers at bay and your cloud safe all through 2025.